Which tests are used to screen for colon cancer?
Colon cancer often develops quietly over several years. In most cases, it begins as small, noncancerous growths in the colon's lining called polyps. Over time, some of these polyps may turn into cancer. Because the disease usually shows no symptoms in its early stages, screening for colon cancer is one of the best ways to detect problems before they become life-threatening. Colon cancer is very treatable and often avoidable when detected early.
Understanding the Importance of Screening
The primary objective of screening is to locate and take out polyps before they develop into cancer. Additionally, early detection of colon cancer increases the likelihood of successful therapy. In general, medical professionals advise those at average risk to start screening at age 45. Individuals may need to start earlier if they have a family history of inflammatory bowel disease, colon cancer, or specific genetic disorders. Your doctor will guide you on when and how often to be screened based on your personal risk factors.
Colonoscopy: The Most Comprehensive Option
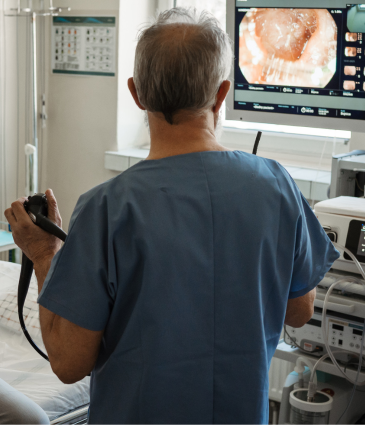
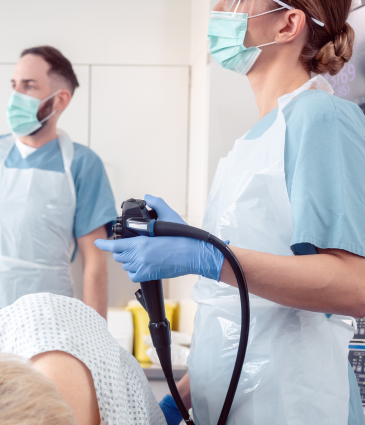
The colonoscopy is often considered the gold standard in screening for colon cancer because it enables medical professionals to inspect the rectum and colon in their entirety. The doctor can get a complete image of the intestinal lining by inserting a thin, flexible tube with a miniature camera into the colon. This test is particularly useful because, if polyps are discovered, they can be taken out immediately to stop the development of cancer. The procedure is done under sedation, so patients remain comfortable throughout. For those with normal results, a colonoscopy is usually repeated every ten years.
Sigmoidoscopy: A Shorter Examination
A sigmoidoscopy is similar to a colonoscopy; however, it simply looks at the colon's lower portion. It is less invasive and often requires less preparation. This test can identify polyps or other abnormalities in the rectum and sigmoid colon. However, because it does not examine the upper colon, it may miss some issues. If abnormalities are found, a follow-up colonoscopy is typically recommended to complete the evaluation.
Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT)
The FIT test is a straightforward, non-invasive method that finds concealed blood in the stool, which may be an early indicator of big polyps or colon cancer. A small sample of stool can be collected at home and sent to a lab for analysis. This test does not require any special diet or bowel preparation, which makes it very convenient. However, if blood is detected, a colonoscopy is needed to determine the cause. Doctors usually recommend taking the FIT test once a year.
Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT)
Another stool-based option is the FOBT, which also checks for hidden blood. Unlike FIT, it may be affected by certain foods, supplements, or medications, so patients are often asked to follow dietary restrictions before the sample is collected. This test is also done annually and can help spot early signs of bleeding in the digestive tract.
Stool DNA Test
The stool DNA test, available under brand names such as Cologuard, checks for abnormal DNA markers shed by cancer or precancerous cells into the stool. It is more advanced than traditional stool tests and can detect both blood and DNA changes. It’s performed every three years and can be done easily at home. A positive result will still require confirmation with a colonoscopy, but it’s a comfortable option for those avoiding invasive procedures.
CT Colonography (Virtual Colonoscopy)
CT colonography, also known as virtual colonoscopy, employs sophisticated CT scans to produce comprehensive images of the colon for those who would rather have a non-invasive imaging option. The procedure is quick and does not require sedation. While it provides a clear view of the colon’s structure, patients still need bowel preparation, and any polyps found must be removed through a traditional colonoscopy afterward. This test is typically repeated every five years.
Screening for Colon Cancer in Turkey
In Turkey, screening for colon cancer is widely available and performed with modern equipment in specialized gastroenterology centers. Many hospitals offer advanced colonoscopy and imaging services at a high standard of care. The costs in Turkey are generally more affordable than in many other countries in the West, attracting patients from abroad seeking reliable, cost-effective screening options.
Conclusion
One of the most effective methods for avoiding and early detection of colon cancer is routine screening. Whether through colonoscopy, stool-based tests, or virtual imaging, the goal is the same: to catch potential problems before they become serious. Take the first step toward safeguarding your long-term health by consulting with your doctor about the screening test that best suits your needs.
- Addiction ( 28 )
- Bariatric ( 2 )
- Cardiology ( 10 )
- Check-up ( 55 )
- Ear Nose & Throat ( 1 )
- Eye Care ( 2 )
- General Surgery ( 3 )
- Gynecology ( 6 )
- Hematology ( 2 )
- IVF ( 19 )
- Neurosurgery ( 6 )
- Oncology ( 15 )
- Orthopedics ( 8 )
- Physiotherapy ( 1 )
- Plastic & Beauty ( 7 )
- Stem Cells & Longevity ( 19 )
- Transplantation ( 4 )
- Urology ( 8 )